Homo habilis 2-2
Habilis. Habitual toolmaker.
* 2.5 to 1 mya.
The first recognised remains—OH 7, partial juvenile skull, hand, and foot bones dating to 1.75 million years ago (mya)—were discovered in Olduvai Gorge, Tanzania, in 1960 by Jonathan Leakey.
* First homo.
* Found in East Africa and South Africa. Lake turkana. Sterkfontein.
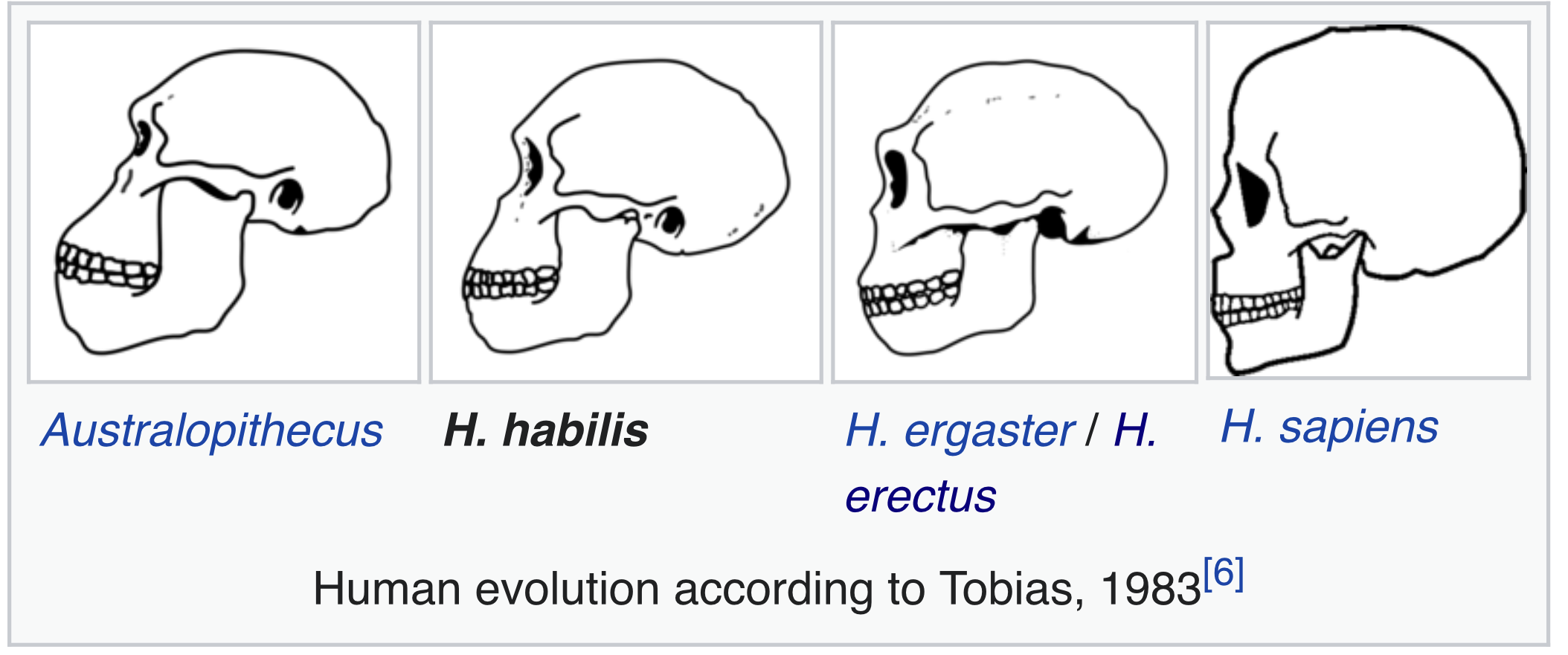
OH 24 or Twiggy in Tanzania 1968 1.8 million years ago. Less protruding face and larger brain.
* OH 7 Tanzania 1960 1.75 million years ago small dental size, increase brain size. Johnny's child. Olduwai gorge.
* Louis leakey Philip Tobias and John Napier studied and described as homo habilis from Tanzania Kenya Ethiopia Malawi and South Africa.
* homo habilis found on eastern side of lake turkana is called homo Rudolphensis. It is bigger than homo habilis.
* Smaller chewing complex and larger brain. Rounded skull. It Tim White studied differences between homo habilis and australopithecine and suggested that australopithecine garhi was its ancestor because says Jaw and teeth are mostly similar. Transition took between 3 and 2.5 million years ago.
* Donald Johnson 1980 discovered skeleton apart from skull. Bipedal short legs in comparison to arms.
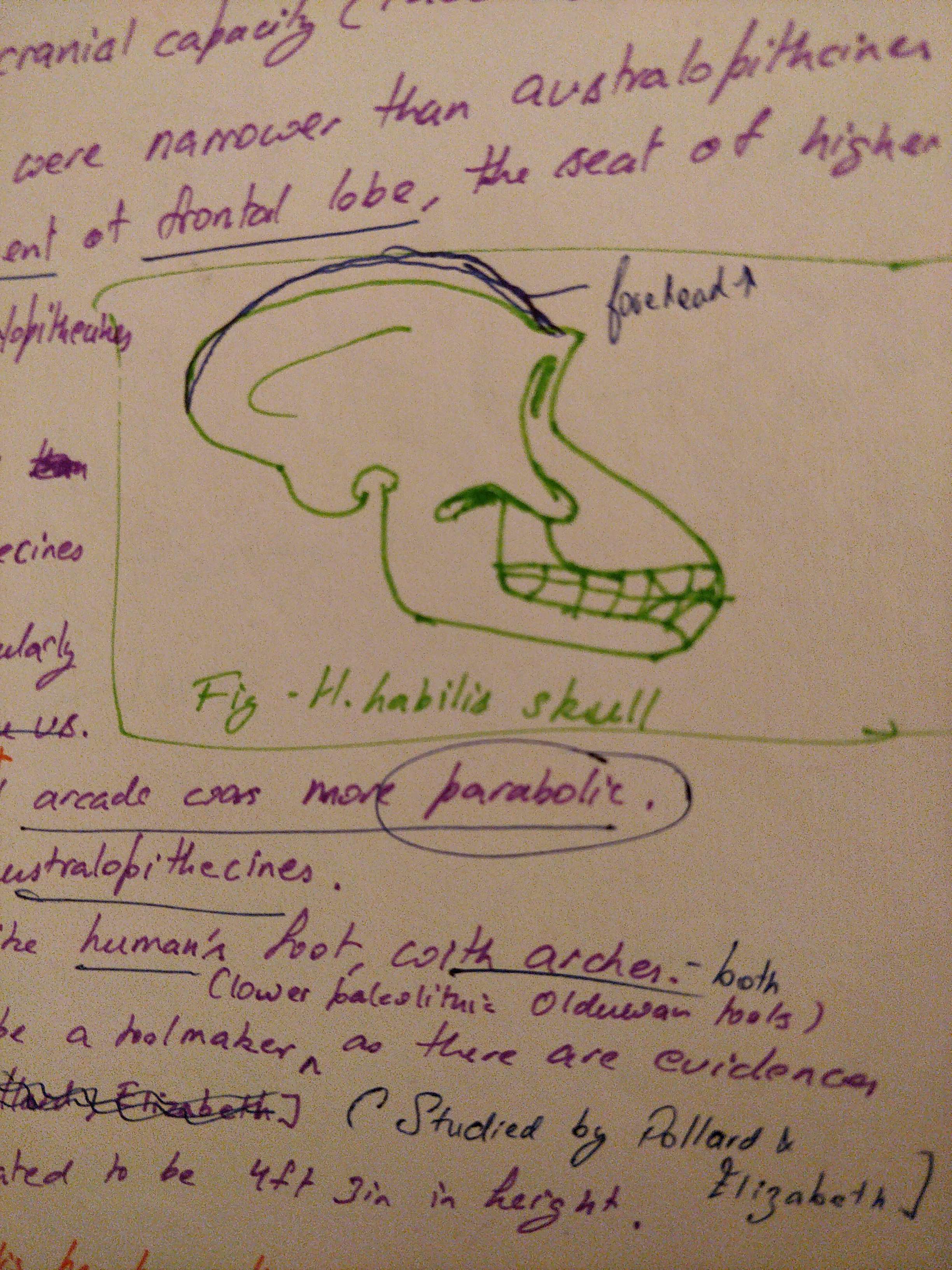
* Intelligence and use of tools. Large brain small chewing muscles and smaller teeth then australopithecines. Dependence on tool used indication.
Premolars with two ridges.
Less massive mandible.
* stone tools are more common in homo habilis sites than australopithecus sites. Cognitive advancement proved by increased tool making and tool used. It tools were fundamental to their survival. Diverse diet.
* warming around 2.5 million years ago increased habitat diversity and increased food resources for homo habilis. Therefore it had died versatility. 2.5mya capacity for speech.
* 650 cc. Long arms. Less protruding face. Parabolic dental arch. Small teeth. 4.3 ft.